- Audio Editing Guide
7 Types of Audio Effects You Should Know
Nov 05,2019• Proven solutions
When it comes to producing music, audio effects are next-level creative tool that you can make use of to create highly enthralling and creative music/videos.
You can either create audio effects of your own or make use of predefined royalty-free audio effects template (if you don’t wish to invest, as a beginner).
Audio effects have the power to transform any so-so music into a superior finished track.
For this reason, we’ve specifically tailored this post to help you understand the insights of audio effects. Moreover, we’re also going to get familiar with 7 types of audio effects that are must be knowing! So, let’s not delay any further and start exploring.
Part 1: The definition of audio effects
Before we get our hands on to the different core types of audio effects, we should first understand what audio effects are!
Basically, the audio effects are generated by software or hardware devices by manipulating the way an audio signal sounds. One can control the Effects with the help of several parameters.
For instance, rate, drive or feedback. They come in handy as studio tools during the mixing or recording music or while playing live.
Here are some core types of audio effects we’re going to discover further in the article.
- Time-based effects include “Reverb” and “Delay and Echo”.
- Spectral effects include the “Equalization (EQ)” and “Panning”.
- Dynamic effects include “Distortion”.
- Modulation effects include “Chorus”.
- And “Filters”.
Part 2: Audio effects - Reverb
Reverb is nothing but an audio effect of a bunch of echoes occurring simultaneously.
In other words, sound reaches your ears in two ways. One that directly reaches your eardrums without any obstacles or surfaces.
And the other, a bunch sound waves that reach your ears after getting bounced off of different surfaces. This set of echoes reach your eardrums later and is quieter (due to lesser energy).

Basically, Reverb stands for Reverberation. It happens quite always in our daily life but we hardly notice it. You may experience different types of reverb audio effects in different types of spaces.
For instance, reverb at tunnels or caves is different from the reverb audio effect of cathedrals or halls.
Reverb audio effects can be generated digitally with the help of reverb plugins to create multiple echoes algorithmically and by manipulating the delay, level or frequency response.
Part 4: Audio effects - Panning
The panning audio effect is generally created to cast an illusion that the source of the sound is moving from one position of the stage to another. This is achieved by distributing the sound signal in a multichannel or a stereo field.
Panning audio effect is highly helpful at instances where you need to avoid muddiness or masking (when two tracks/sounds overlap each other) in your mix. You can position the sound artificially, to a specific area of your stereo field.
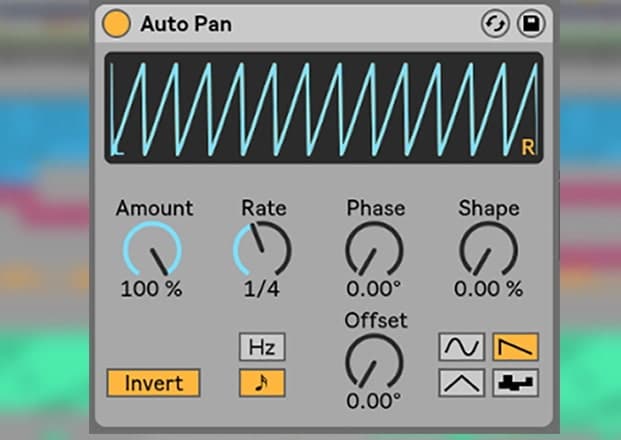
With the help of auto-pan, you can define the time span during which the sound must sweep across the stereo field.
Usually, the lead elements like vocals or the low-frequency elements like bassline drums panned to the center. This is because the center is the busiest and also these sound elements ground your mix.
Part 5: Audio effects - Equalization
The sound frequency that falls into the range from 20 to 20,000 Hz is the audible sound spectrum of human ears. With EQ technique, this spectrum is split into different sections referred as bands.
These bands are then used to either subdue or enhance the fragments of a mixed track.
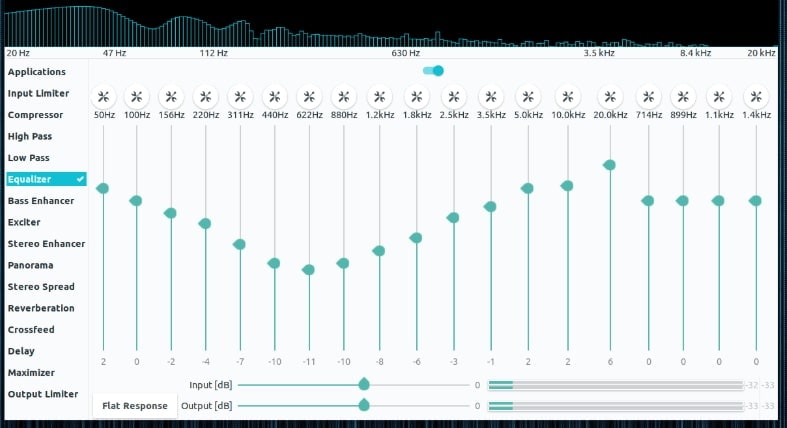
Remember, EQ-ing works on existing spectrum only by altering the fragments to create novel-sounding effects. EQ audio effects are majorly used to define a character or tone of the soundtrack.
Moreover, you can define different types of sound characters with the help of different EQ audio effects. For instance, a digital plugin EQ is far more transparent sounding when compared to a vintage EQ.
Part 6: Audio effects - Delay and Echo
Delay is yet another type of audio effect that falls under the Time-based category. It can significantly provide more complexity and depth to a soundtrack by adding layers.
The foundation to add reverb or chorus-like other audio effects is furnished by Delay. Hence, it is prominently utilized by several mixing engineers.
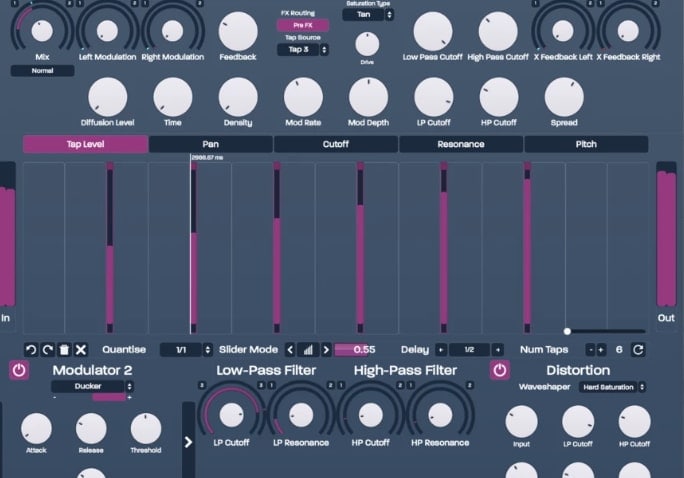
Echo is too falls under the time-based audio effect, which is developed due to the Delay audio effect. An echoing effect is simulated at various intervals when Delay audio effect features playback heads or “taps” that are heard apart.
Part 7: Audio effects - Distortion
When an audio circuit is overloaded that, ultimately, lead to clip the signal is what is termed as Distortion.
This audio effect can actually be a highly creative tool if used in the right manner. Distortion pushes the sound to compress and clip by manipulating the original audio signal.
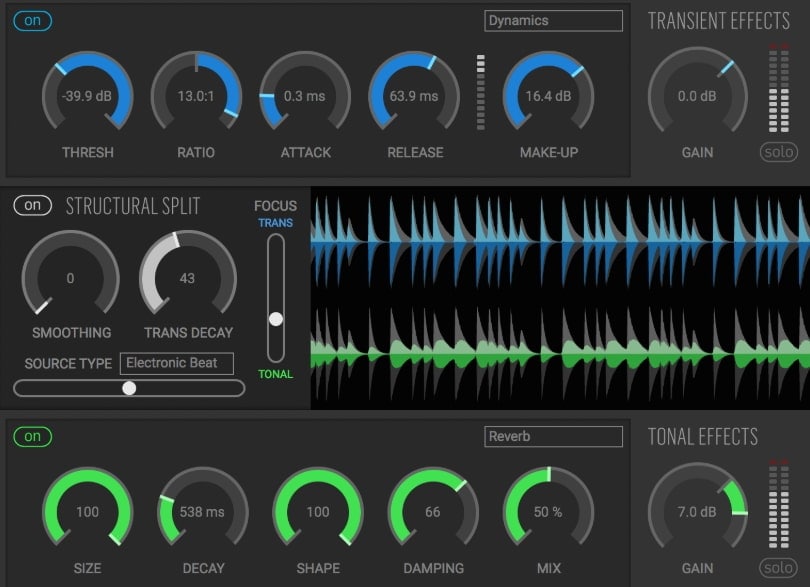
By manipulating the bit rate or the sampling rate, Bit-crushing is achieved. This, eventually, adds harmony to the sound.
Usually, the electric guitars make use of Distortion audio effect but more progressively it is being used over Synths.
Distortion can be acquired using effects units, rackmounts, pedals, VSTs or at times, built-in amplifiers and pre-amps. Distortion adds complexity and body to your track by making it fatter and fuller.
Part 8: Audio effects - Chorus
Chorus audio effect is referred to the varying sounds that are similar and are heard as one.
For instance, recording the same note piled over each other and is timed and tuned slightly off each other.
This as a whole creates a chorus effect. In simple words, a group of singers are voicing a song at the same time creating a singular sound effect.
The chorus too adds complexity and depth to your soundtracks. It is generally used to enhance the harmony or load up the particular track which, in turn, makes the track fuller and layered.
Part 9: Audio effects - Filters
An audio signal’s frequency range can be altered using the Audio filters. With the help of an audio filter, you can easily amplify or boost the frequency range.
Or, can even cut or attenuate a frequency range too. When it comes to categorizing the Audio Filters, they fall under 3 units; HPF (High-pass filters), LPF (Low-pass filters), BPF (Band-pass filters).
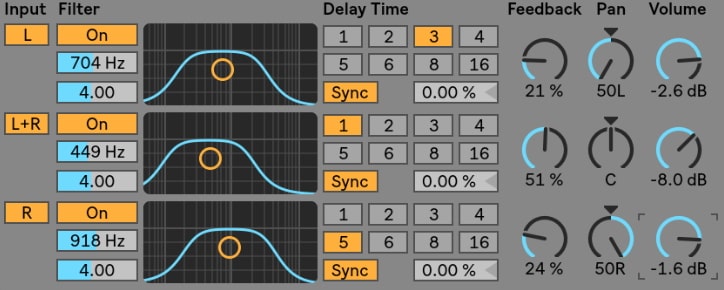
Every other filter has a well-defined threshold for boosting or cutting a frequency. They are then categorized depending on the alterations have been made above or below this threshold.
An Audio filter is a prominent tool used to correct problems and to enhance tracks significantly. With filters, you can effectively make dramatic effects or add character to the soundtrack.
Conclusion
With this comprehensive discussion done on audio effects and various core types of audio effects, it’s now time to conclude this topic. We now believe you have a full understanding of these core audio effects and can effectively make use of them as per your needs.
Bring up your video to a professional level with straightforward tools.
Try It Free Try It Free




Benjamin Arango
staff Editor
0 Comment(s)